Pegasus

Northrop Grumman Successfully Launches Pegasus XL Rocket for the US Space Force
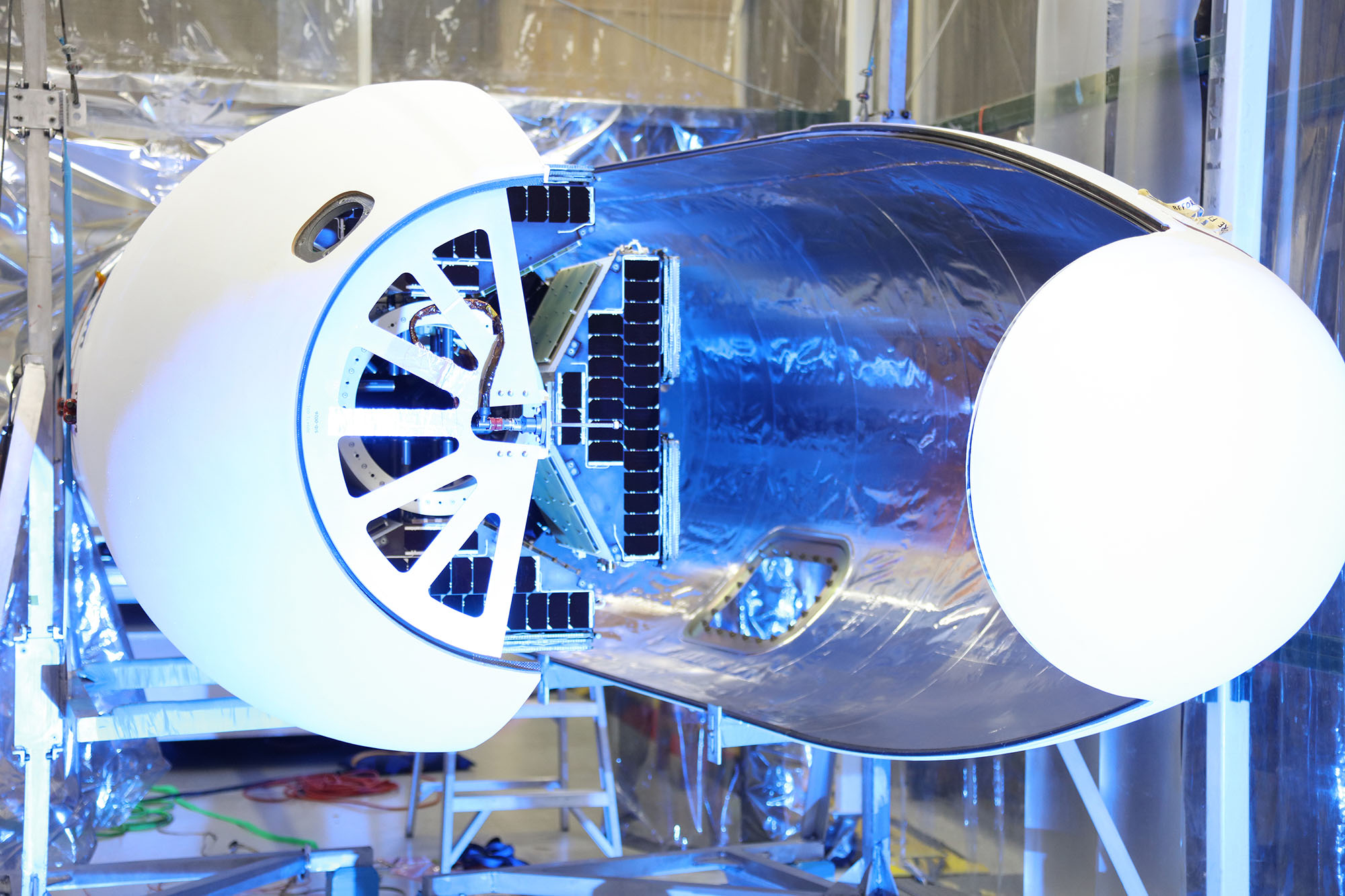
Pegasus Rocket
On April 5, 1990, a new era began in commercial space flight when the Pegasus rocket was launched from beneath a NASA B-52 aircraft in a mission that originated from Dryden Flight Research Center in California. In the decades since its maiden flight, Pegasus has become the world's standard for affordable and reliable small launch vehicles. It has conducted 45 missions, launching nearly 100 satellites.
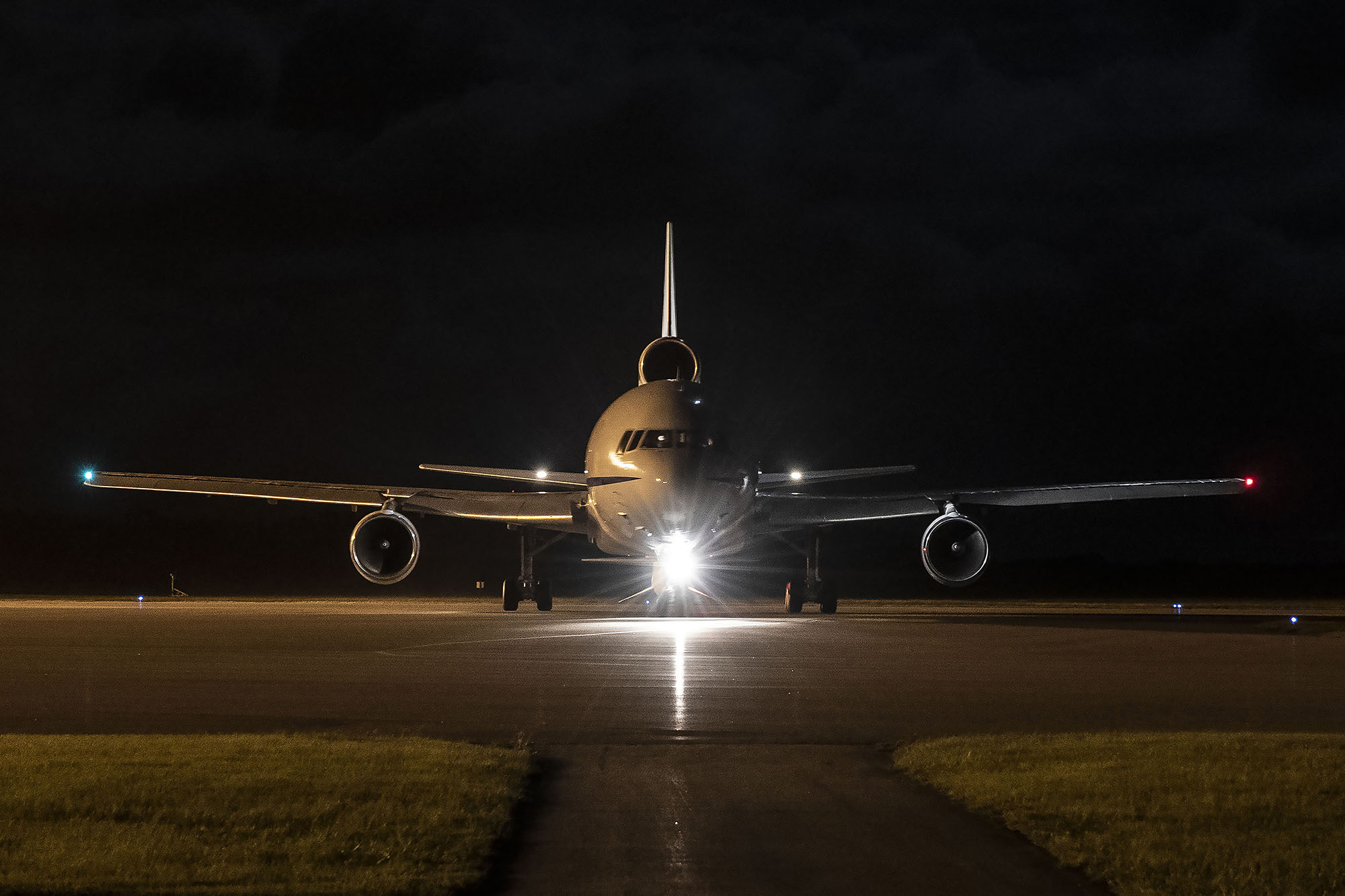
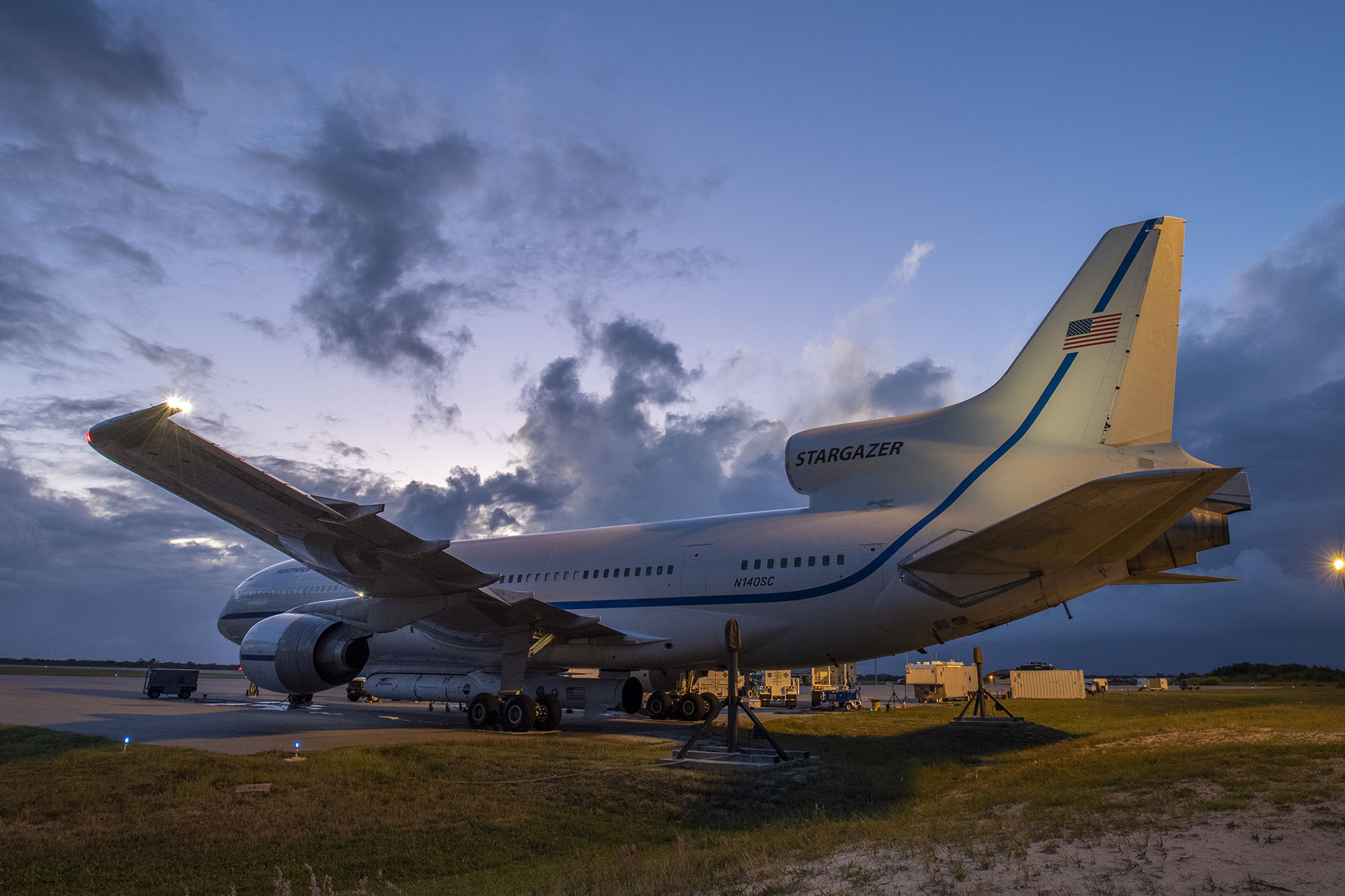
The three-stage Pegasus rocket is used to deploy small satellites weighing up to 1,000 pounds (453.59 kg) into low-Earth orbit. Pegasus is carried aloft by our Stargazer L-1011 aircraft to approximately 40,000 feet over open ocean, where it is released and free-falls five seconds before igniting its first stage rocket motor. With its unique delta-shaped wing, Pegasus typically delivers satellites into orbit in a little over 10 minutes.
This patented air-launch system provides customers with unparalleled flexibility to operate from virtually anywhere on Earth with minimal ground support requirements. Pegasus launches have been conducted from six separate sites in the U.S., Europe and the Marshall Islands, the first time a space launch vehicle has demonstrated such operational flexibility. Pegasus XL is a category 3 NASA-certified vehicle.
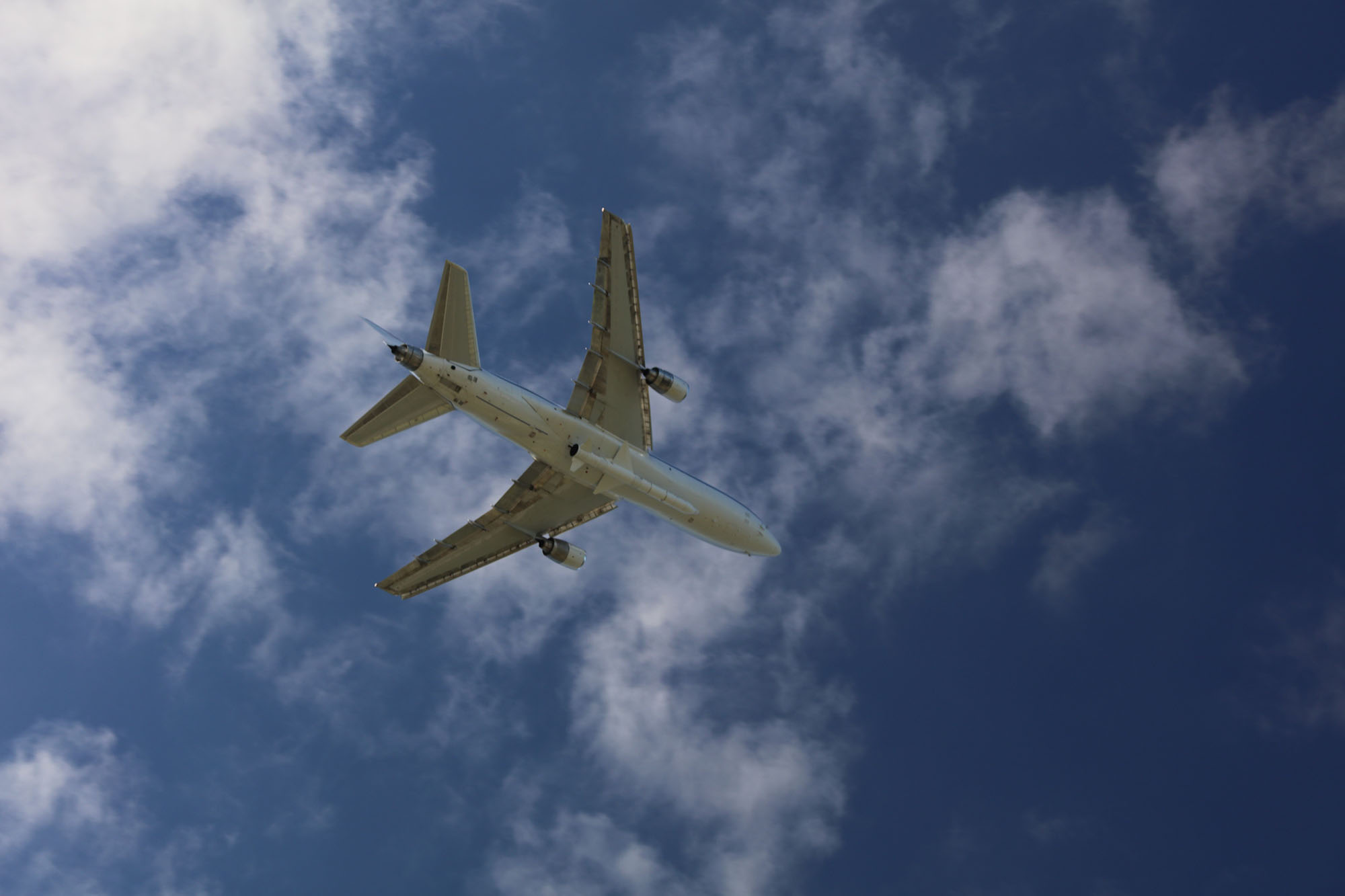


Pegasus Defines Possible
In the decades since its maiden flight, Pegasus has become the world's standard for affordable and reliable small launch vehicles.
- World's first privately developed space launch vehicle.
- First winged vehicle to accelerate to eight times the speed of sound.
- First air-launched rocket to place satellites into orbit, using its carrier aircraft as an "air breathing reusable first stage."